A microscope lets us peer into this world. This article reviews Monocular, Binocular, and
Trinocular Microscopes features and how to Elect Among Monocular Binocular Trinocular Microscopes.
It also describes types of observations these Microscopes is suited for and main Differences Between a Binocular and a Trinocular Microscope.
Monocular, binocular, and trinocular head types are designed differently and suited for particular types of observations.
Type 1.
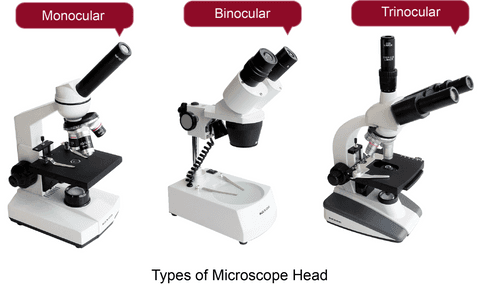
Monocular Microscopes
Monocular microscopes have a single tube that houses an eyepiece at one end and an objective lens at the other. The design means that specimens will appear flat and without depth when you look in the eyepiece.
Monocular microscopes are easy to use and ideal for classrooms or as a home microscope for kids and teens.
Type 2. Binocular Microscopes
Binocular microscopes have two tubes and eyepieces, and this can make it more comfortable to examine specimens. Binocular head pieces can be used in educational, research, and commercial settings.
Type 3. Trinocular Microscopes
Trinocular microscopes are similar to binocular ones except that they have an extra port for attaching a camera and taking photographs or videos. This makes the trinocular head type ideal for educators or researchers.
Main Differences Between a Binocular and a Trinocular MicroscopeA monocular microscope is not so prevalent, and the least used one. So, we’ll look at the main differences between a binocular and a trinocular microscope, which you must consider while purchasing.
1. Number of Eyepieces
An eye piece’s core aim is to focus the light rays and provide a specimen’s magnified image. A binocular microscope with two eyepieces can give high range magnification up to 80x to 40x, and a trinocular microscope can give up to 1000x magnification on average.
Higher magnification depicts better microscopic results of the specimen.
2. Light SourceThe microscope’s efficiency depends on the amount of light it receives, enhancing the microscopic image result’s clarity.
A binocular microscope gets light passing through an illuminator present at the bottom of the microscope. In contrast, light is reflected directly towards the eyepiece in a trinocular microscope, followed by the camera.
More a microscope is capable of obtaining the light; further, the magnification results can get better. Thin slides of microorganisms require optimum light to give a spectacular view.
3. Camera Support
Having a camera supported in microscopes is a very advanced yet useful feature in a microscope. It allows you to capture your final results and use them in the future.
Binocular microscopes comprise only one camera eyepiece, which allows the placement of an external camera on the head that has to be replaced after working.
In contrast, a trinocular microscope has two-camera eyepieces and an established internal camera port that is not needed to replace and gives you a hassle-free experience during your microscopy.
4. Objective Lenses
An objective lens is responsible for giving a high-magnification and fair resolution image result of the specimen and determines the microscope’s entire efficiency.
Binocular microscopes have three to four powerful objective lenses with average magnification levels that distinguish the real desired image and give the closest view.
A trinocular microscope offers around five bright
objective lenses with optimum magnification range, enhancing the specimen’s image transparency.
Monocular, Binocular or Trinocular Microscopes, which one do you perfer? Comment below to share your thoughts on this blog post.

 Binocular microscopes have two tubes and eyepieces, and this can make it more comfortable to examine specimens. Binocular head pieces can be used in educational, research, and commercial settings.
Binocular microscopes have two tubes and eyepieces, and this can make it more comfortable to examine specimens. Binocular head pieces can be used in educational, research, and commercial settings.

















